Examination of 4 Different Genes

The Four Obesity Genes
There are four genes related to obesity which we will examine and analyze: three genes commonly associated to obesity and one gene found to also be related with obesity. These genes are β3AR, UCP1, PRARGC1A and β2AR.
Understanding these genes will point out the relationship between a person’s gene type and the diet suitable for them.
The Role of the Gene
DNA is the blueprint of life. As such, organisms like plants, animals and also humans are made up of 3 billion base pairs of DNA. In the 3 billion base pairs in humans, there are sites involved in shaping our body called “genes”. The variation in genes make up the differences in our eye and hair color, nose, height, ear shape and other various parts of our body.
The influence of genes is not limited to our physical appearances. For example, our blood type, athletic ability and sensitivity can also be influenced by our genes. Recently, there was even a development on genetics regarding our susceptibility to diseases.
Various studies from different countries have established that certain genes are related to obesity and thus, the study of genes has been an important factor in addressing obesity.
Genes Involved in Obesity
There are genes that have roles such as in forming the “design” of our bodies these are said to be deeply related to obesity.There are also other genes which play a role in our ability to metabolize carbohydrates, lipids and calories.
By analyzing these genes, we can examine various factors such as our ability to metabolize carbohydrates and lipids, our accumulation of visceral and subcutaneous fat, and the rate of our basal metabolism. Based on the results, experts in DNA will analyze your body’s gene composition whereas experts in pharmacy and nutrition will propose effective diet methods and plans for you.
Introducing the Four Obesity Genes
-


A gene involved in carbohydrate metabolism. If there is a mutation in this gene, carbohydrate metabolism tends to be lower.
In addition, this gene is responsible for the activation of the brown fat cells which helps in burning fat. If there is a mutation in this gene, it is less likely for fat to be burned and there is a tendency to accumulate visceral fat around the stomach.Mutation Rate
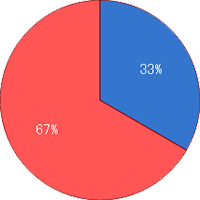
No mutation=67%
With mutation=33% -

A gene involved in lipid metabolism. When there is a mutation in this gene, lipid metabolism tends to be lower.
In addition, this gene is involved in the production of energy in brown fat cells. When there is a mutation in this gene, burning of fat is less likely to occur due to the tendency for subcutaneous fat to accumulate in the lower body.
Mutation Rate
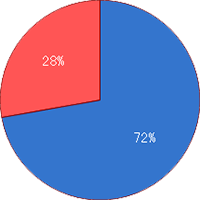
No mutation=28%
With mutation=72% -


A gene involved in the production of heat in mitochondria. When there is mutation in this gene, the tendency to produce and generate heat in mitochondria during exercise is less likely to occur.
There is a tendency for the mitochondrial heat production to be difficult and for energy consumption during exercise to not easily yield effect when there is a mutation in this gene.Mutation Rate
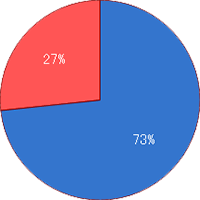
No mutation=27%
With mutation=73% -

A gene involved in protein metabolism and muscle condition. When there is a mutation in this gene, there is also faster protein metabolism and hardening of muscles is more likely to occur.
Also, when mutations in this gene are involved, the resting basic metabolic rate and basal metabolic rate tend to increase.
Mutation Rate
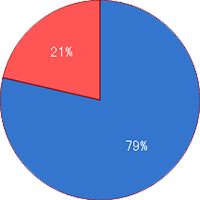
No mutation=21%
With mutation=79%
![]()

